Got it Active ingredient in cordyceps is cordycepin
Extracts of the fungus Cordyceps sinensis have been shown to boost testosterone levels and improve the endurance capadity of the over 50s in lab tests. Now it looks as though researchers at Hung Kuang University in Taiwan have worked out at least which active ingredient in Cordyceps is responsible for the rise in testosterone: cordycepin.

Cordycepin is an adenosine analogue. Cells have receptors for adenosine, which can raise and speed up metabolism of cells. Because adenosine receptors play a role in the production of testosterone in Leydig cells, the researchers decided to test this substance on mice and the testosterone producing Leydig cells of mice.
In the first experiment young mice aged 5-7 weeks were given injections of cordycepin in their small intestine every day for seven days.
The daily dose was 40 mg/kg bodyweight. Cordycepin had no effect on bodyweight or the prostate; it did have an effect on the weight of the testes and the concentration of testosterone. The testes increased in weight by 6 percent, and the testosterone concentration rose by 391 percent.
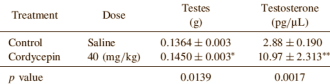
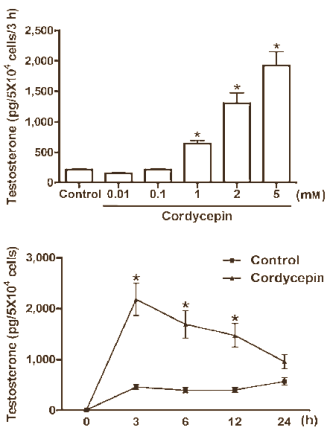
Experiments with Leydig cells showed that the maximal effect of cordycepin was reached within three hours. The higher the concentration of cordycepin, the more testosterone the cells produced.
When the Taiwanese researchers added cordycepin and various adenosine blockers to Leydig cells, they were able to work out that cordycepin works most via adenosine receptor A2a [production increased by a maximum of factor 7], and to a lesser extent via A1 and A3.
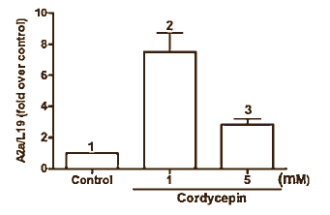
The researchers were able to show that via the adenosine receptors cordycepin raises the concentration of cAMP and via cAMP the activity of the STAR protein.
The Taiwanese are cautious, stating that cordycepin is only one of the active substances in Cordyceps sinensis and Cordyceps militaris.


 您当前的位置:
您当前的位置:
 沪公网安备31010102008381号
沪公网安备31010102008381号